2.3. Company & Management
2.3. Company & Management
2.3.2. Business system, organisation chart, corporate goals
Managing a company means running a business with structural and procedural organisation. In order to successfully organise a business idea in competition, a business system must be developed. The business system model describes the main activities of the enterprise in its structural composition. It is about the value chain of the enterprise. The way of producing services, the sequence of work processes, the rational design of the business organisation including payment and personnel management must be determined.
![]()
Note: Every company needs a specific business system. The value creation process for a start-up is structured differently than that for a medium-sized production company or that for a trading or service company.
Management and organisation chart
With the decision of the ownership structure, the management of the enterprise is defined. With the determination of the process flow, the organisation of the employees based on the division of labour and the responsibilities are to be determined. In the case of partnerships, the owner is the decision-maker and the managing director at the same time. He can also appoint a third party to manage the enterprise.
In corporations, the ownership and management of a company are usually legally separate. In a corporation, management is the responsibility of one or more managing directors or a board of directors. Management is responsible to the owners for the overall running, including profit-making, of a business. Managers act on behalf of the owners like entrepreneurs.
company structure is usually represented in an organisation chart This defines the persons with their functions, tasks, and responsibilities. There are different forms of organigrams. An example of a staff line function is shown:
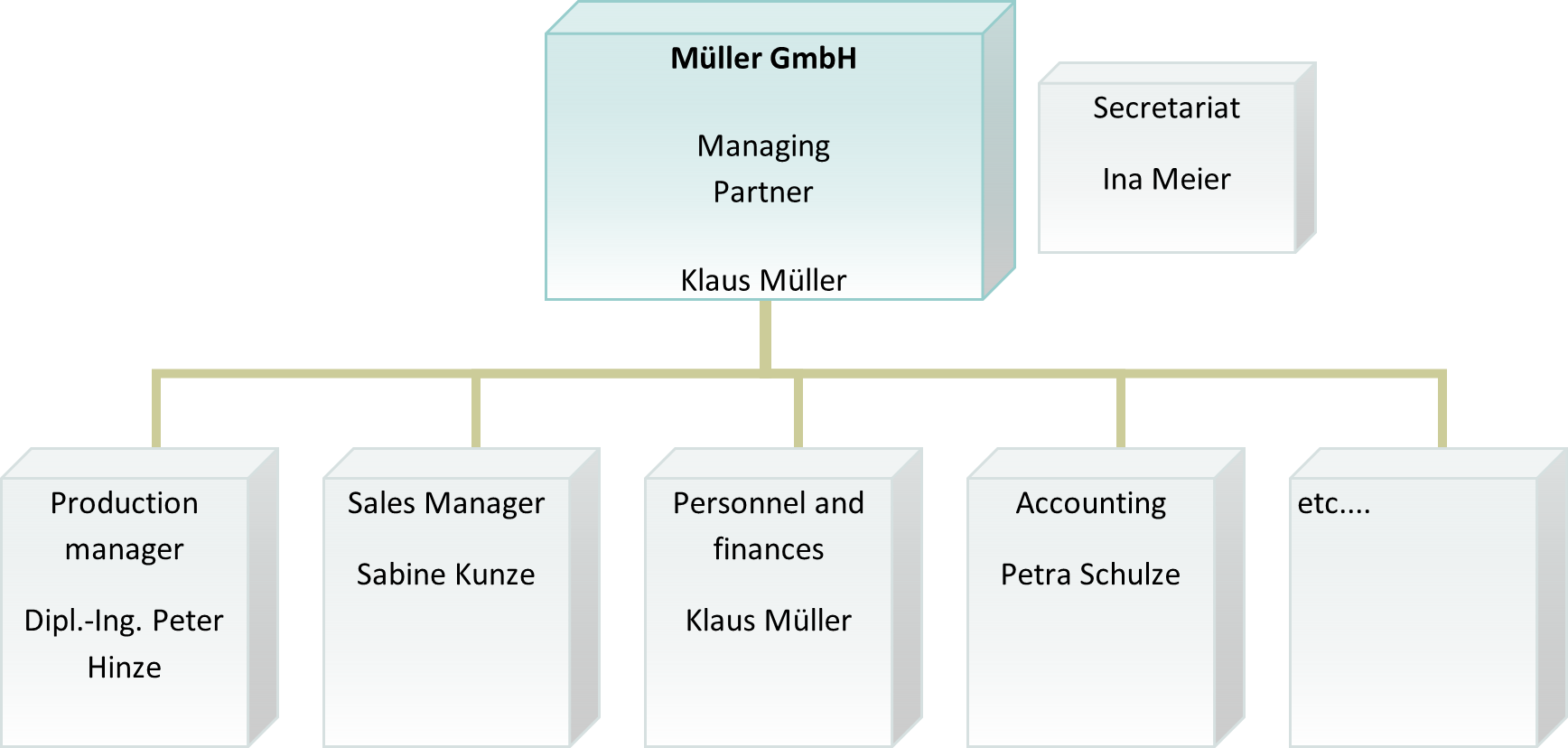
Corporate goals
One of the basic operational decisions is that the entrepreneur must define the goals for his business. The business goals are determined by the founders and investors. With the formulation of goals, the strategic orientation is formulated as well as the operative actions in the company.
The corporate strategy is the definition of the entrepreneurial intention, where and how the company wants to stand in the market in the future (3 to 5 years)
A distinction can be made between long-term and short-term corporate goals. Strategic goals are mostly long-term. In the operational area, the short-term goal description is helpful.
objective can be subdivided into overall, intermediate objectives and sub-objectives as well as formal and factual objectives.
The formal objectives include the definition of entrepreneurial success This is measured in terms of turnover, profit, and liquidity targets. The material objectives provision of services in terms of type, quantity, quality, place, and time
The business objectives must be formulated in a business plan in such a way that they are measurable and thus verifiable. This means that they must be operationalised.
The top priority in a business plan is the annual turnover and profit targets. These are calculated concretely with the sales and turnover forecast. The targets are to be determined for the first three years. They should be oriented towards growth. The turnover and profit targets must be justified. They have strategic significance for the company.
Liquidity planning is existential for the company. The liquidity targets are to be defined as corporate goals. The amount of liquidity is determined in the liquidity calculation.
The material goals include quantitative and qualitative goals for the production of goods and services. Quantity to be produced, quality, continuous performance improvement, customer orientation, the conquest of regional markets, the acquisition of new target groups, the completion of a significant project, the improvement of employee motivation or a new Internet presence If a new product is to be introduced to the market or the price structure is to be changed, intensive preparations are required.
However, the definition of the goals in the business plan alone is not sufficient. The desired business objectives must be justified.
Defining turnover and profit targets is particularly difficult for start-ups because they do not yet have sufficient experience with their businesses. One must be warned against "high" profit expectations. High is a relative term, and it is open to interpretation. In reality, many companies make a few percentage points of profit on turnover (e.g., 2 % - 8 %). In a few cases, more than 10 % or even 20 % profit on turnover is achieved.
In the first months or even up to two years, company targets can also define losses from turnover. The turnover targets are determined with the help of the sales and turnover forecast. The profit/loss targets are determined with the P&L statement. Commercially sound planning is the basis for a successful business plan.
When defining long-term corporate goals perspective is important If you want to become the market leader and challenge the market leader, you will only achieve your goal in differentiated process steps and corporate goals. The goals must correspond to the development status of the company, then they have a high plausibility.